Broadband Internet Troubleshooting: 100% Solid Tips
[ad_1]
We often only care about broadband Internet troubleshooting when there’s no connection. But of course! There’s no need to do anything when all is well.
You can’t Google how to troubleshoot the Internet connection when you, well, have no Internet — and when you call the support line, many providers tell you to visit their troubleshooting page. The point is it’s a good thing you’re reading this now when you’re still connected.
Before continuing, make sure you understand that Wi-Fi and Internet are two different things.
Aso, this post focuses mostly on the Internet connection. If you want to troubleshoot your Wi-Fi connections, check out this post on Wi-Fi dropping and connection issues.
Dong’s note: I first published this post on Jan 18, 2019, and updated it on April 17, 2022, to add more relevant information.

Broadband Internet Troubleshooting: Four simple steps
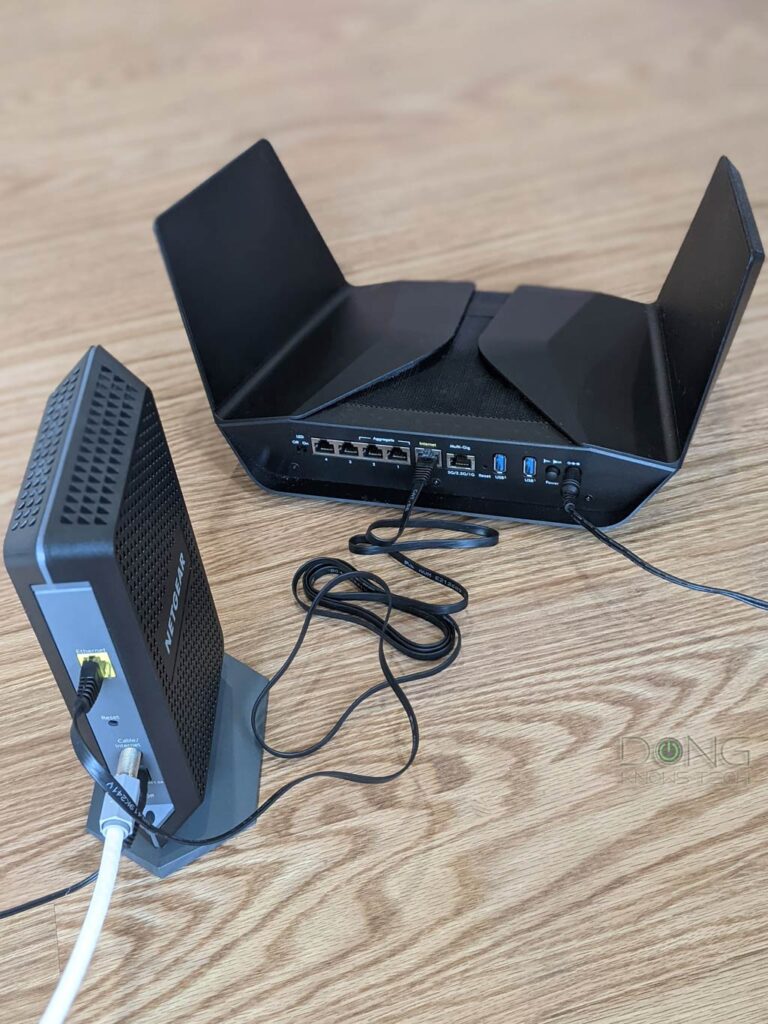
Every network is different. Most importantly, you need to know if yours consists of a set of a terminal service and a router or a gateway. The latter is a device with a terminal device and a router inside a single hardware box.
To find out which is which, you can consult this post on home networking hardware.
But with all of them, you can apply these steps when you don’t have a Wi-Fi connection or have no Internet access. Often, the issue is minor and requires as little as a restart of the router or modem.
1. Take care of the basics
These are basic things you should do first before anything else.
The service (or website) might be unavailable
If you can’t go to a particular website or a service, the first thing to do is try a few different ones to see if they work.
That’s because many times, the specific site or service is unavailable. This website you’re reading, for example, has an up-time rate of 99%, which is relatively high but not 100%.
In this case, that has nothing to do with your home network or the Internet. The same idea applies when you can’t access Netflix but can still stream from YouTube. All you can do is wait it out or call the particular service provider to find out more.
Your device’s Wi-Fi might be turned off
Make sure you haven’t accidentally turned off the Wi-Fi on the device.
This applies to laptops where you might switch on the Airplane mode by accident. It’s also rather common in media streamers and IoT devices.
Also, some Wi-Fi router has an on/off switch for the Wi-Fi function — make sure it’s in the on position.
Which Wi-Fi network you’re using?
That’s right. Ensure your device connects to the correct Wi-Fi network (and not one of your neighbors, for example.)
Connecting to the wrong Wi-Fi network will cause local tasks — such as network printing or file sharing — to fail.
Most importantly, you’d be troubleshooting something that’s not necessarily broken.
Are the cables intact and plugged in securely?
Indeed. Check to make sure all the cables and wires are plugged in properly and intact — not cut, broken, or chewed up by pets.
All hardware devices (router, modem, ONT, gateway, switches, etc.) must be plugged into power and turned on. At the very least, you should see some lights coming out of them.
2. Figure out where the issue is
When all the cables are in good shape, it’s time to find out where the problem is.
- Can you connect to your Wi-Fi network? If you can’t, or your network is unavailable — you don’t see the Wi-Fi name on your phone — the router is the issue.
- Suppose you can connect to your Wi-Fi network. When your computer or phone indicates that there’s a Wi-Fi connection, you cannot access the Internet to check email or Facebook. The issue is likely at the terminal device — that’s your modem or ONT.
In any case, you can always start with the modem/ONT.
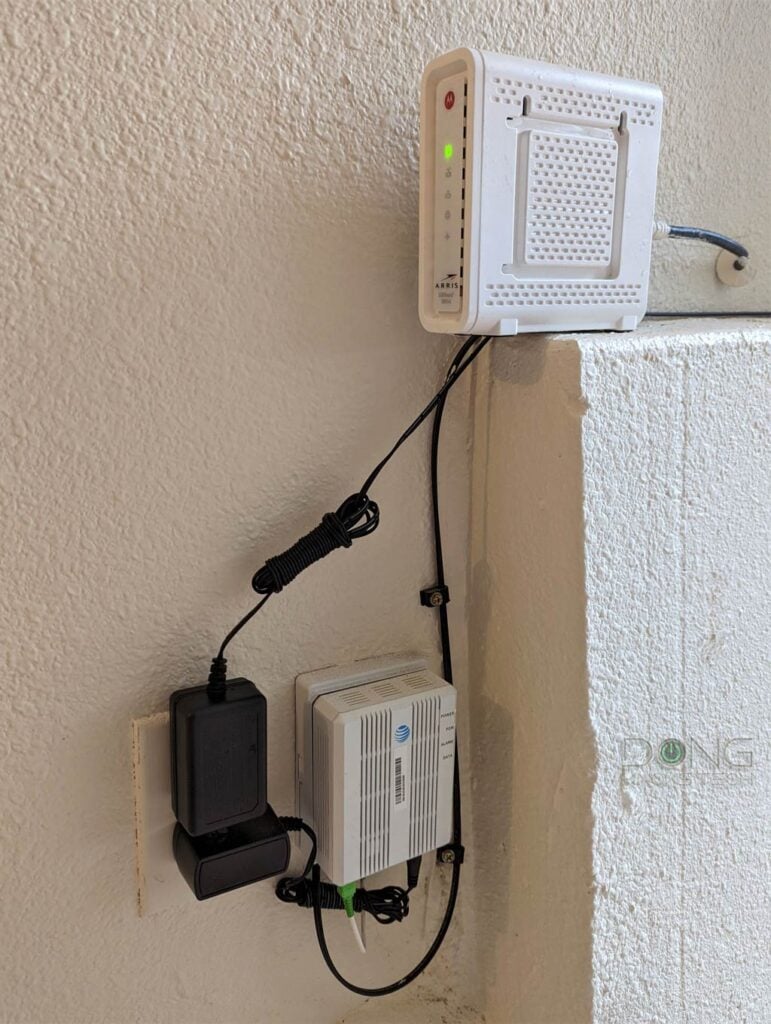

3. Broadband Internet troubleshooting: How to check the terminal device.
Your terminal device is your connection to the Internet. It needs to be in good shape. But if you use a modem, things are slightly different from when you use an ONT.
What to do with a modem
No matter what device you use, it always has a broadband status light.
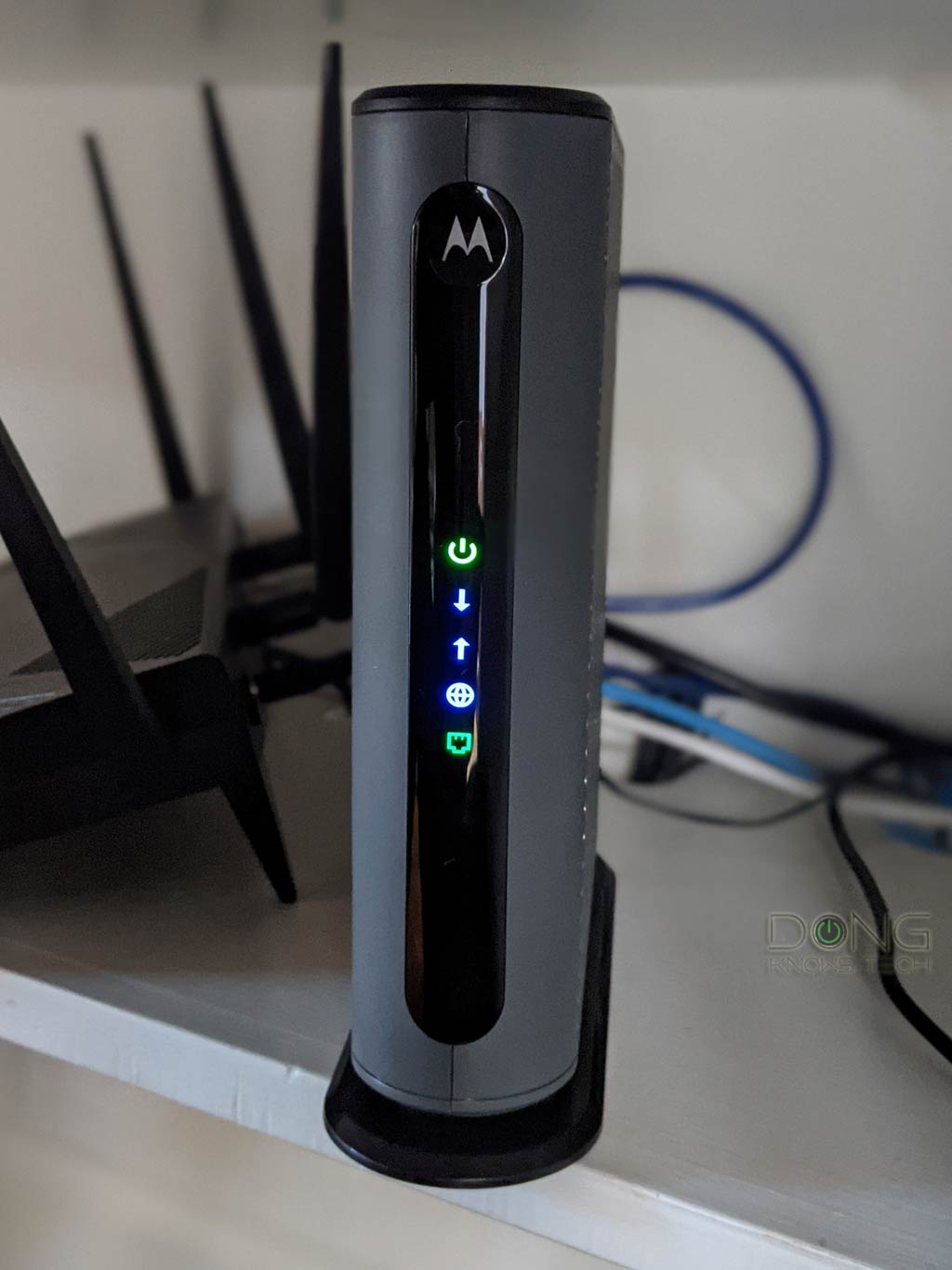
In most modems, such as the Motorola MB8600 below, this light tends to have a shape or a label that suggests that it has something to do with the Internet. Often it resembles a little globe or the letter E.
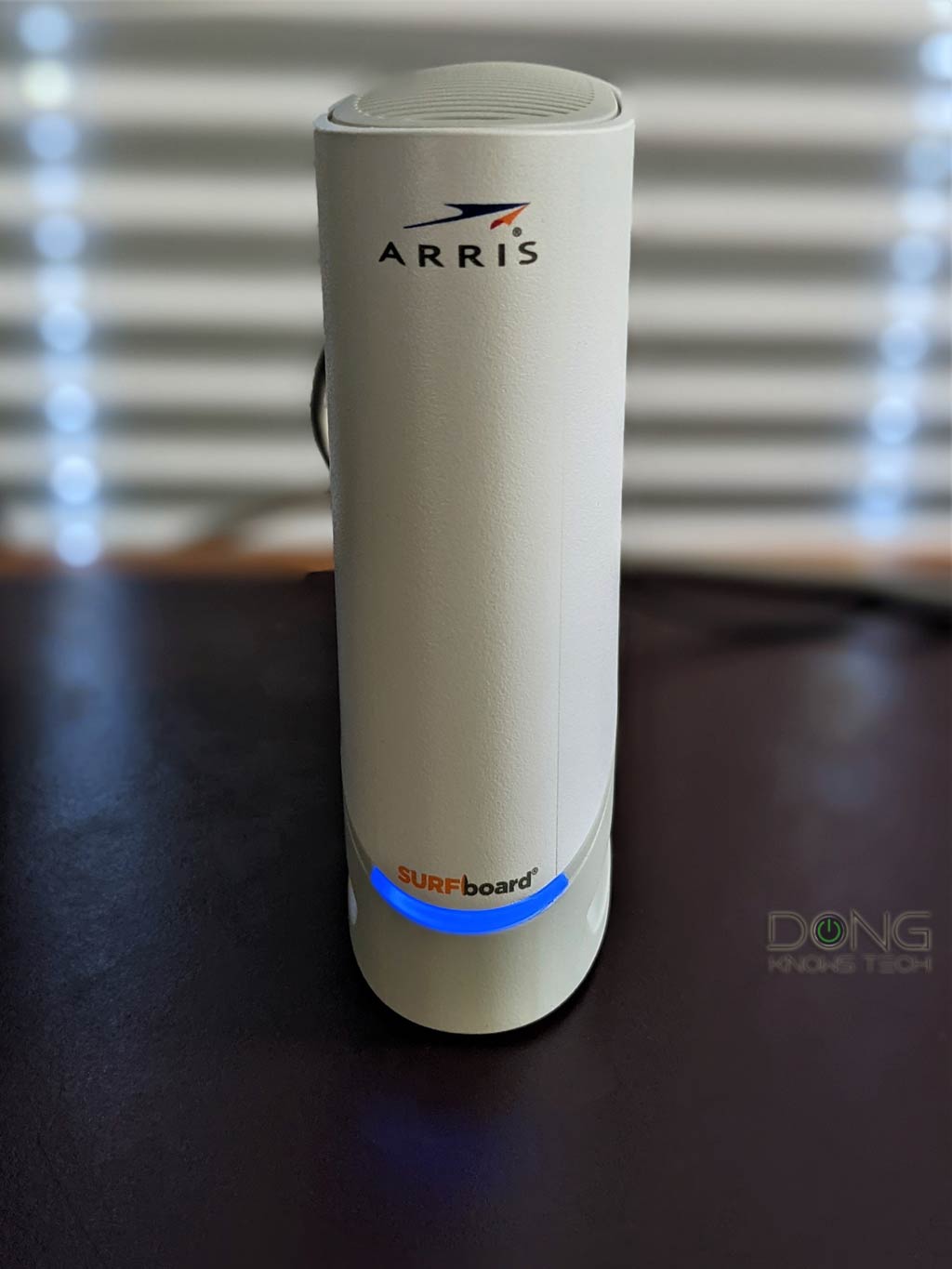
However, some modems, such as the ARRIS SURFboard S33, come with a single light that changes color to show the status. In this case, you must remember what color means for the Internet connection.
In any case, here is what you can do at the modem.
- Give the modem a restart, then wait a few minutes for it to boot up fully. Often that fixes the problem. (If the modem is hard to reach, you can do this via its web interface. Almost all modems use the 192.168.100.1 default IP address.)
- Check the broadband status light. It must show the correct color. In a traditional modem, the broadband light needs to be solid (green, blue, or white). If it’s off, red, or flashing erratically, ensure the service cable is intact and securely attached to the device.
If that doesn’t fix the issue, check to ensure there’s no outage in the area.
If nothing works and there’s no outage, it’s time to call your provider. At this point, there’s nothing you can do. Tell the customer support agent that you have no Internet signal at the modem. They’ll know what to do.
What to do with a Fiber-optic ONT
A Fiber-optic ONT is even more simple than a modem, but it also has a broadband light often labeled as PON or a star symbol.
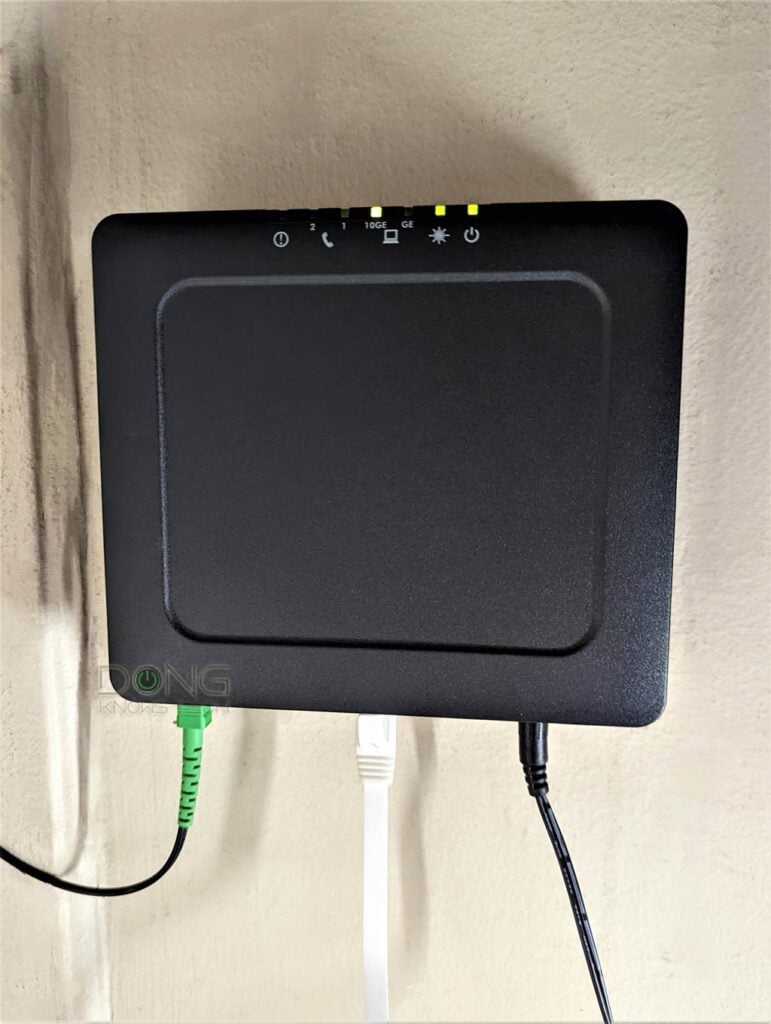

This particular ONT in the photo can also deliver a second Gigabit connection (not in use) and two phone lines (not in use).
This light has to be solid. After that, make sure the Ethernet shows the connection status between the ONT and a router’s WAN port is also in good shape.
There are two things you can do to troubleshoot an ONT:
- Restart the ONT itself — unplug it from power and plug it back in.
- Reset the Fiber-optic service line — remove it from the ONT and then re-connect it.
In the photos above, the black cable is for power, and the green one is the service line.
If that doesn’t fix the issue, it’s time to call the provider.
4. Wi-Fi issues: What to do at the router
There are a couple of things you can do with the router. There are simple and advanced steps.
Simple things you can do with a router
These are steps anyone can do.
- Give the router a restart — unplug it from power, wait for 10 seconds or so, then plug it back in. Now give it a few minutes to boot up fully. That might fix the issue.
- Ensure the router’s Wi-Fi function is not turned off — many routers have an on/off switch for Wi-Fi. Generally, the router has a status light for its bands (5GHz and 2.4GHz). These lights need to be on.
Advanced steps in working with a router
These are general steps for advanced users or those comfortable with computers.
- Access the router’s web interface. Try updating its firmware to the latest.
- Access the router’s interface gain. This time, back up its settings, then reset it — yes, I do mean reset — and set up your network from scratch (or restore it from the backup file).
| Vendor | Friendly URL | Default IP | Username | Password |
| Asus | router.asus.com | 192.168.1.1 192.168.50.1 |
admin | admin |
| AT&T Gateway | n/a | 192.168.1.254 | n/a | Access code printed on the hardware unit |
| Comcast (Xfinity) Gateway |
n/a | 10.0.0.1 10.1.10.1 |
admin cusadmin |
password highspeed Access code printed on the hardware unit |
| D-Link | dlinkrouter.local | 192.168.0.1 192.168.1.1 |
n/a | admin |
| Netgear | routerlogin.com | 192.168.1.1 | admin | password |
| Linksys | myrouter.local | 192.168.0.1 192.168.1.1 |
n/a | admin |
| TP-Link | tplinkwifi.net | 192.168.0.1 | admin | admin |
| Most Cable Modems | N/A | 192.168.100.1 | n/a | admin password default |
If you can’t access the interface or don’t know how to reset it using the interface, you can reset it via the reset button. If all that doesn’t solve the problem, it’s time to get a new router or professional help.
Broadband Internet troubleshooting: How to get help
When you call for help, the person on the other end will try to troubleshoot the problem.
It would help if you told them exactly what has happened instead of what you think has happened or how you feel about what happened. Also, describe the issue instead of its consequences.
In other words, don’t give the person on the other end stuff that has no technical information. Examples: “I can’t get online,” “my internet doesn’t work,” “my computer doesn’t work,” “my Wi-Fi is not working,” etc.
Instead, be descriptive and explain exactly what happens. Such as, when I go to an XYZ website, I get an ABC message. Or give the person the error message or what you see on the hardware, such as the statutes, lights, etc.
It’s also helpful to take and share photos of the error messages and the device’s status lights. Visual is always useful when it comes to troubleshooting.
The takeaway
Internet, like all things in tech, is technical and dry. The best way to deal with them is to understand how things work. Getting frustrated or taking things personally won’t help.
Here’s the silver lining: If you pay attention and follow the instructions, it’s almost a guarantee that you can fix it. For this reason, dealing with machines is almost always easier than dealing with the emotions of our kind. I speak from experience.
[ad_2]
Source link





